Human Thyroid Aging
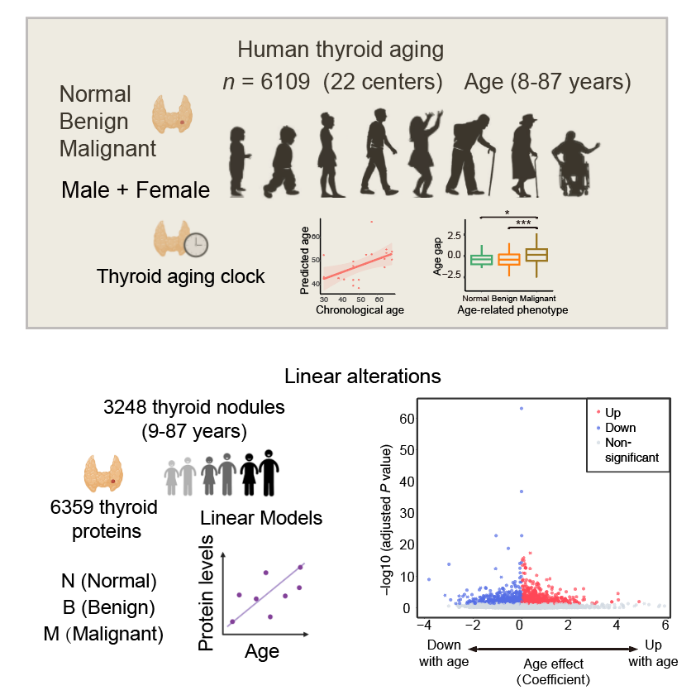
Aging is a complex biological process characterized by the progressive decline in physiological function and increased susceptibility to diseases, making it a major risk factor for life-threatening diseases. Organ-specific diseases are linked to the accelerated aging of corresponding organs. Aging mechanisms in thyroid pathophysiology require systematic characterization and may provide actionable insights for delaying thyroid aging, preventing and treating thyroid tumors, and promoting healthy aging in the population.
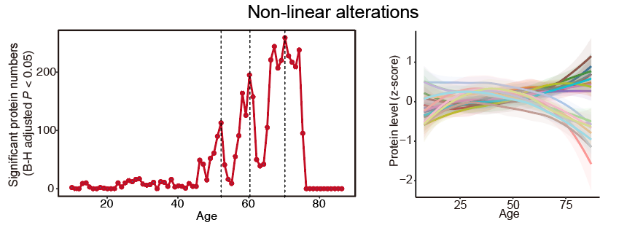
We collected 6109 normal and various benign and malignant thyroid tumor tissues from 22 medical centers and performed label-free deep proteomics analysis of both human and mouse thyroid tissues. We built an aging clock based on proteins from normal thyroid tissues and validated the model and measured biological ages of tumor thyroid tissues in three independent datasets, exploring impact of tumors on thyroid aging. We identified age-associated proteins and pathways, both linear and non-linear, linked to metabolism, immune response, and extracellular matrix organization.
Supported formats: XLSX
Download Example FilesPlease ensure that the column names (protein names) are consistent with those in the demo data, and they should include the 95 proteins from the aging clock. The row names should correspond to the sample names. Additionally, the matrix requires feature normalization (z-score).
Output
| Sample name | Biological age of the samples |
|---|
Linear alterations
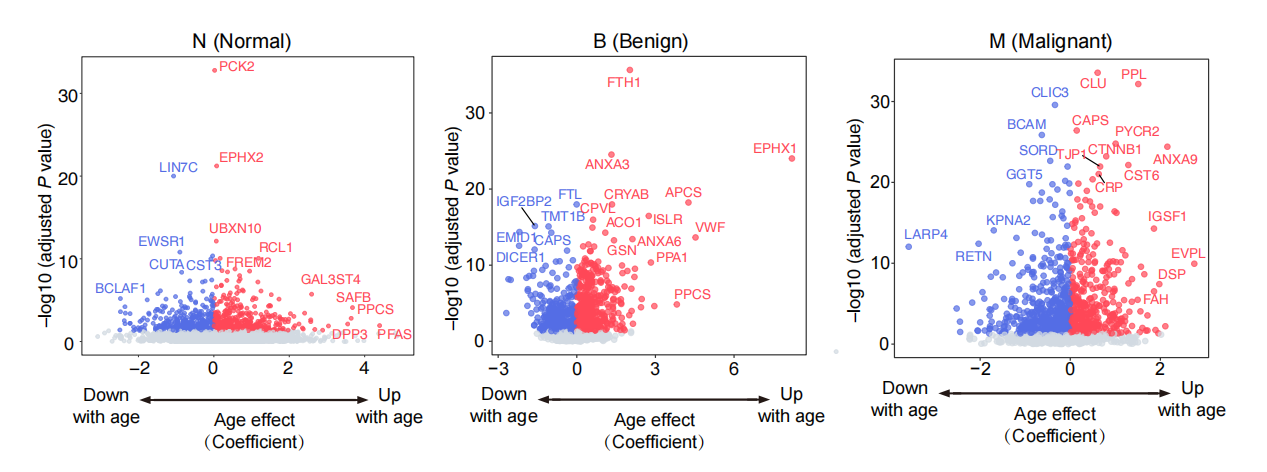
| Type | Coefficient | P value | adjusted P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|